Antlia
Welcome to the Antlia Page!
Antlia is a small, faint constellation located in the southern skies. Its name is an ancient Greek word for “the pump.” The constellation was originally named Antlia Pneumatica, to commemorate the invention of the air pump, which it represents.
Antlia was created and catalogued by the French astronomer Abbé Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in the 18th century, along with 13 other constellations introduced by Lacaille to fill the void in some faint regions in the southern sky. Lacaille’s constellations are mostly named after scientific instruments and there are no myths attached to them.
FACTS
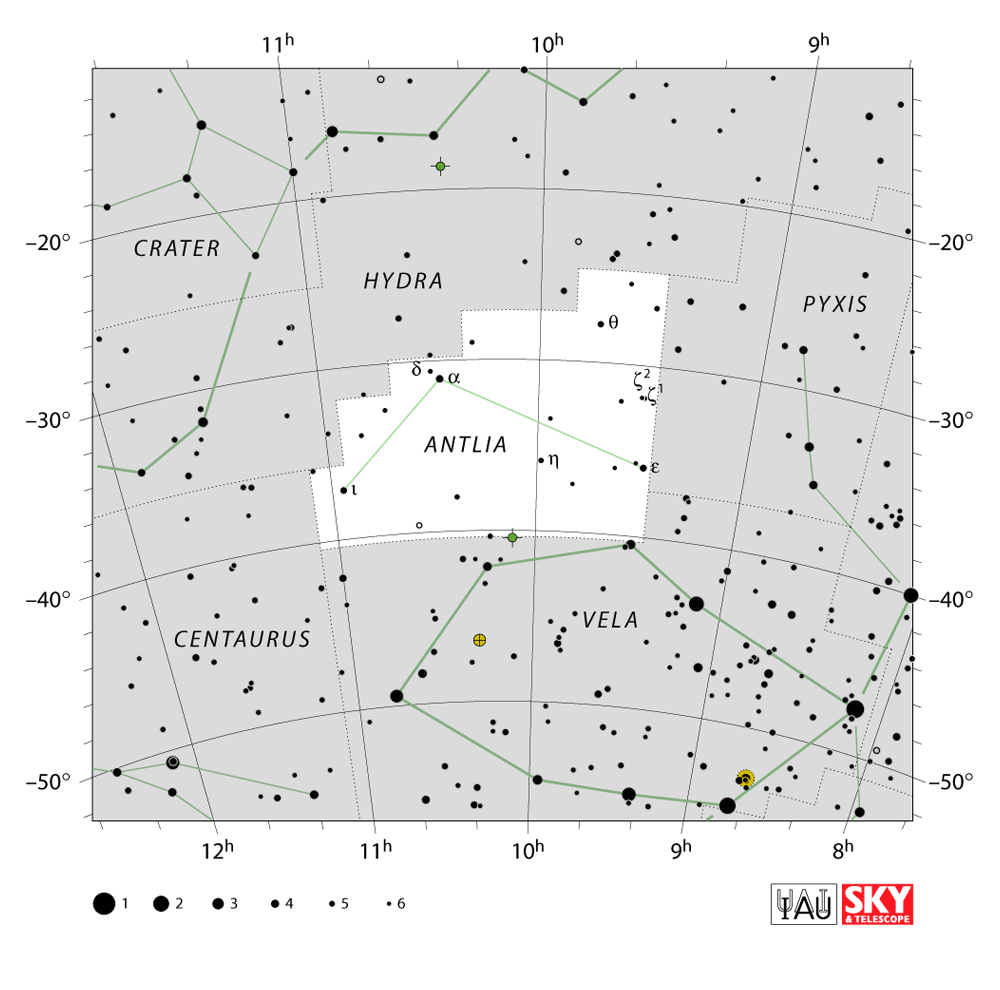
Antia is one of the smaller constellations in the sky (62nd in size), occupying an area of 239 square degrees. It is located in the second quadrant of the southern hemisphere (SQ2) and can be seen at latitudes between +45° and -90°. The neighboring constellations are Centaurus, Hydra, Pyxis, and Vela.Antlia does not have any stars brighter than magnitude 3.00. It contains two stars located within 10 parsecs (32.6 light years) of Earth.Andromeda is the 19th largest constellation in the sky, occupying an area of 722 square degrees. It is located in the first quadrant of the northern hemisphere (NQ1). Andromeda can be seen at latitudes between +90° and -40°. The neighboring constellations are Cassiopeia, Lacerta, Pegasus, Perseus, Pisces and Triangulum. Andromeda has three stars brighter than magnitude 3.00 and three stars located within 10 parsecs (32.6 light years) of Earth. The brightest star in the constellation is Alpha Andromedae, also known by its traditional name, Alpheratz. The nearest star is Ross 248 (spectral class M6V), also known as HH Andromedae, found at a distance of only 10.30 light years from Earth.
The brightest star in Antlia is Alpha Antliae. The nearest star in Antlia, DEN 1048−3956, is a brown dwarf only 13.15 light years distant from Earth. Antlia has two stars with known planets, HD 93083 (spectral class K2V) and WASP-66 (F4V). There are no meteor showers associated with Antlia. The constellation does not contain any Messier objects.
Antlia belongs to the Lacaille family of constellations, along with Caelum, Circinus, Fornax, Horologium, Mensa, Microscopium, Norma, Octans, Pictor, Reticulum, Sculptor, and Telescopium. Notable deep sky objects in Antlia include the Antlia Dwarf Galaxy, the Antlia Cluster of Galaxies, and the unbarred spiral galaxy NGC 2997. Antlia also contains the spiral galaxies NGC 3244 and IC 2560 and the interacting pair IC 2545.Andromeda belongs to the Perseus family of constellations, along with Auriga, Cassiopeia, Cepheus, Cetus, Lacerta, Pegasus, Perseus, and Triangulum. It contains three Messier objects – Messier 31 (Andromeda Galaxy), Messier 32 and Messier 110.
Members of the Antlia Cluster include the massive elliptical galaxies NGC 3258 and NGC 3268, the elliptical galaxy NGC 3260, lenticular galaxies NGC 3269 and NGC 3267, the spiral galaxy NGC 3281, and the barred spiral NGC 3271, which is the brightest spiral galaxy in the cluster.
STORY
Antlia does not have a myth associated with it. It was named after the air pump, Antlia pneumatic, an instrument invented by the French physicist Denis Papin, who is also famous for inventing the steam digester, which preceded the steam engine and the pressure cooker.
As depicted by Lacaille, Antlia represents the single-cylinder pump that Papin used in his experiments in the 1670s.
The constellation Antlia was first catalogued in Lacaille’s Coelum Australe Stelliferum, published in 1763, after his death. The catalogue included almost 10,000 southern stars, 42 nebulous objects, and 14 new constellations, now known as the Lacaille family.
